Resistive (4-, 5-, 7- and 8-wire)
Sensor Materials
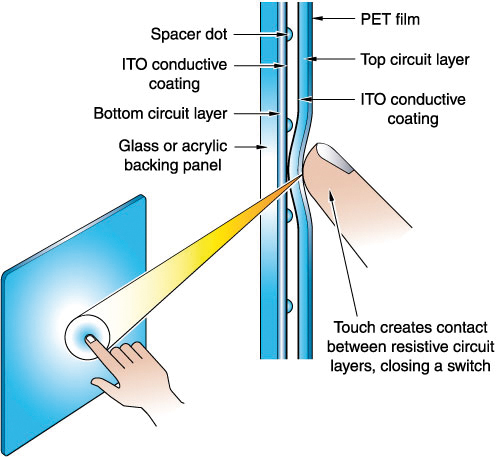
Glass or Acrylic substrate, Spacer dots, Polyester sheet(s)
Principle of Operation
- A touch compresses the flexible Top layer into contact with the bottom glass layer.
- A voltage gradient is applied to the top and bottom layer (X and Y axis) sequentially.
- The controller calculates the X and Y position of the touch based on the voltage gradient applied to one side and using the opposite side as a voltage probe.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
| Most widely used touch technology | PET top sheet is highly susceptible to scratches, cuts and cigarette burns |
| Can be activated by bare finger, gloved hand, or stylus | PET layer is a flexing mechanical element coated with a conductive |
| Low cost | Transmission typically in 80 % to 85 % |
| Limited to two resolvable points; three or more resolvable points requires |
Content and images of 3M were reproduced with permission © 3M 2010. All rights reserved.