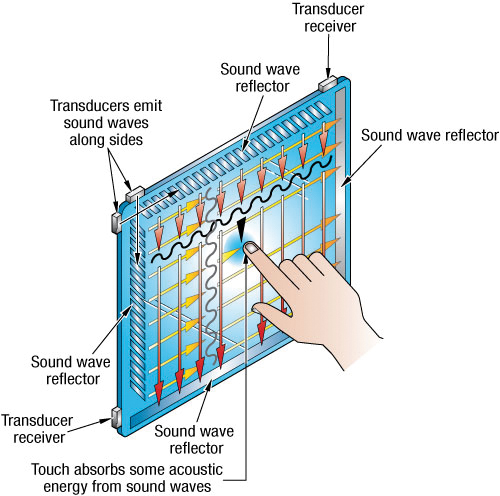
Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW)
Sensor Materials
Glass, piezoelectric transducers
Principle of Operation
- Piezoelectric transmitters on the sensor generate acoustic waves on the surface of the glass substrate on alternating X-axis and Y-axis patterns.
- The acoustic waves are reflected by a pattern of edge ridges directing the energy to piezoelectric receivers.
- A touch to the surface of the sensor causes attenuation to a portion of the wave corresponding to touch position.
- Touch location is based on the time delay from the transmitted pulse to the center of the attenuation area of the wave.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
| Touch activated by bare finger, some gloves, or soft conductive stylus | Moving liquids or solid particles of contaminants may cause false touches or areas without touch function until they are completely removed |
| Light transmission typically 92 % | Dirt and water seal can be difficult |
| Typically wide border | |
| Limited to 1 resolvable points |
Content and images of 3M were reproduced with permission © 3M 2010. All rights reserved.